For this post, we’re featuring an interview with two members of NAVER’s Healthcare AI team: Jaedeok Lee and Hyejeong Jo. What began as internships has evolved into full-time research positions for these dedicated professionals, who are now contributing to the development and advancement of healthcare AI models at NAVER Cloud. Driven by a sense of responsibility and a commitment to technological innovation, they are pursuing AI research to bring meaningful transformation to healthcare environments.
How the journey began
Jaedeok: My goal has been to create new value through AI technology. When I discovered NAVER Cloud was recruiting for LLM application research, I recognized an opportunity to work with a company that had developed its own proprietary LLM. Currently, I focus primarily on the CLOVA Voice EMR service.
Hyejeong: During my Master’s program, I researched LLM applications in healthcare AI and have always been interested in translating theoretical concepts into practical solutions. When I had the opportunity to engage with the Healthcare AI team’s Voice EMR service at NAVER Cloud, the timing seemed ideal. The team was seeking developers to build medical LLMs, which complemented my research background well. Now, as an LLM research engineer, I develop AI features for a ward agent and investigate how AI can enhance medical environments.
Life as a healthcare AI researcher
Jaedeok: My week typically begins with reviewing weekend experiments, followed by a team meeting. These meetings bring together colleagues from frontend, backend, planning, and modeling to discuss current challenges and solutions. I find these collaborations invaluable because genuine research involves tackling unsolved problems. By brainstorming together and studying research papers from diverse fields, we often discover valuable insights that can be adapted to our specific challenges in healthcare AI.
Hyejeong: I start my day by going over research papers and technical materials shared by colleagues and staying current on industry trends. My mornings are dedicated to project development, and I receive code reviews that have significantly improved my skills. These reviews have taught me that good code isn’t just functional—it’s readable and clear, which has helped me develop as an engineer.
In the afternoons, I participate in modeling meetings where we share progress and discuss solutions to the problem at hand. My colleagues offer practical suggestions such as “Have you considered this approach?” or “What about using this tool instead?” This experience has shown me that research isn’t a solo endeavor. Having a team to provide feedback and alternative perspectives helps us make progress more efficiently than any of us could individually.
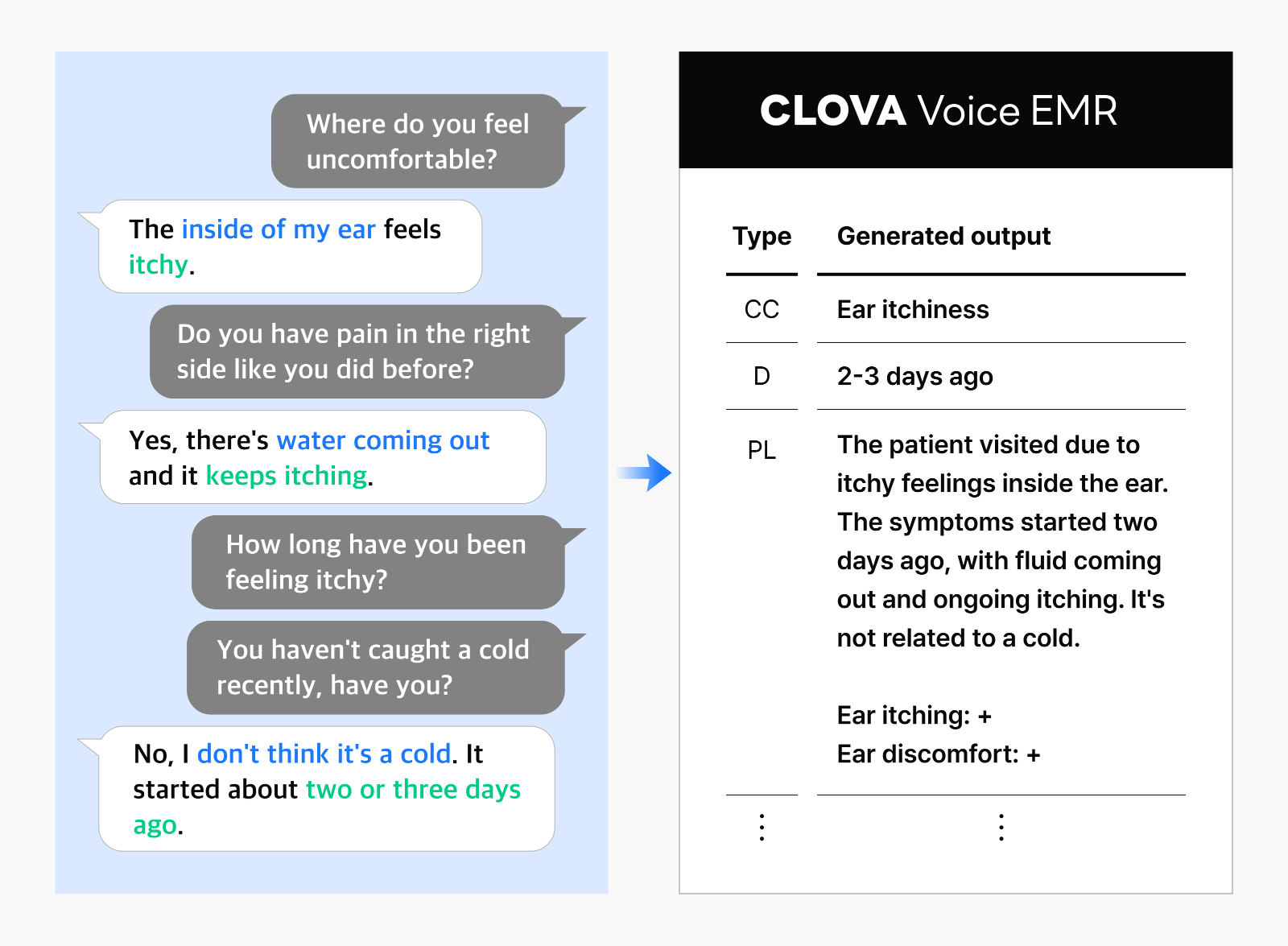
CLOVA Voice EMR: A lightweight model that deciphers any patient speech
CLOVA Voice EMR is a service that transforms doctor-patient interactions through real-time conversation analysis and automated medical record creation. Powered by NAVER’s hyper-scale AI model and advanced voice recognition technology, it enables doctors to monitor documentation as it happens and delivers well-organized, appropriately titled medical records immediately after each appointment.
Jaedeok: Patients commonly report waiting an hour for just three minutes with their doctor, often without proper eye contact as physicians focus on their screens. The average doctor sees 34 patients daily—an extraordinarily demanding workload—and in medical settings, missed information can directly impact care quality. This challenge becomes even more pronounced in emergency rooms, where patients may be too distressed or ill to articulate clearly. This is where AI becomes transformative. For CLOVA Voice EMR to work effectively in these high-pressure settings, our team developed a lightweight model that excels at deciphering difficult speech patterns through background noise while maintaining accuracy.
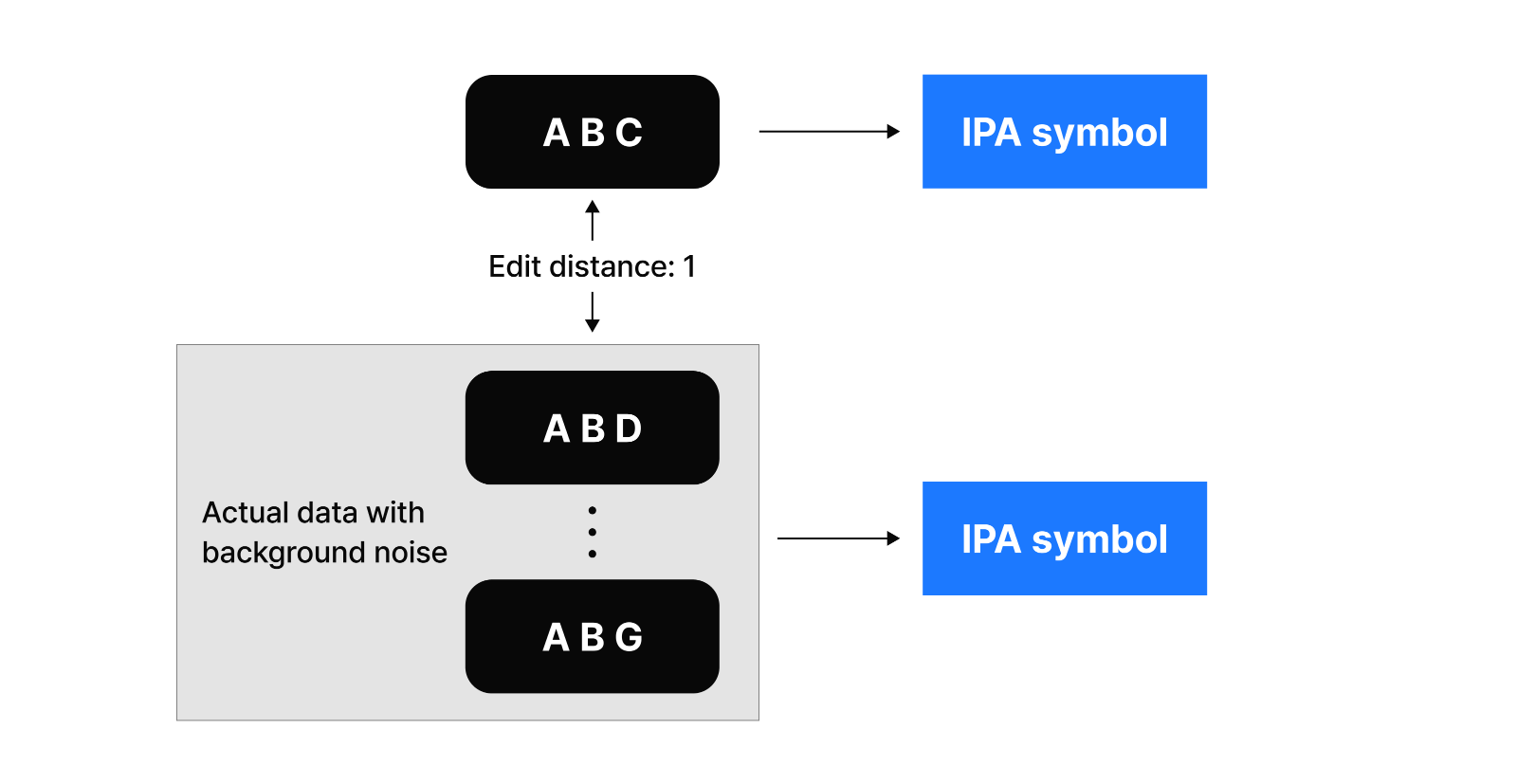
To address speech recognition challenges, we deliberately added noise to clean data and created various mispronunciation scenarios for training purposes. For example, with clear speech like “ABC,” we introduced variations using edit distance—”ABD” differs from “ABC” by just one letter, giving it an edit distance of 1. We then converted these variations to International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) notation to measure pronunciation similarities. This methodically constructed training data helps our system recognize and interpret real patient speech patterns. Despite its compact size, this lightweight model responds remarkably well to noise and, when evaluated specifically on data filtering capabilities, even outperformed LLMs.
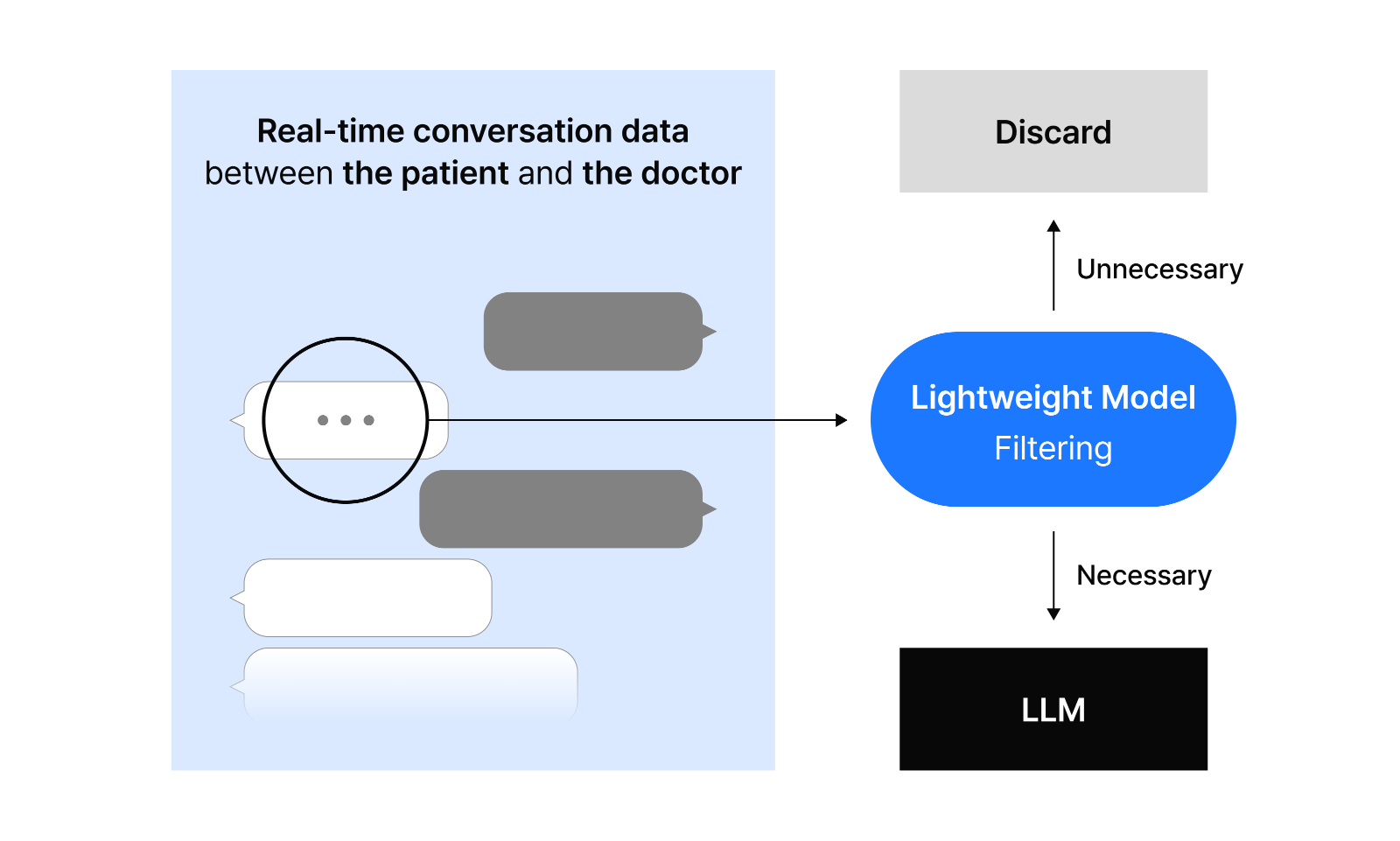 In a real hospital scenario, when a patient says, “My body’s giving me the shivers,” our model can identify the clinically relevant “chill” from the word “shivers.” Even if mispronounced as “shivvers,” the model still recognizes that this conversation contains information pertinent to chills. As doctor-patient conversations happen in real time, all speech is processed by the lightweight model first. When terms like “shivvers” emerge, the model determines if this represents essential clinical information—if important, it’s sent to the LLM for deeper analysis; if not, it’s discarded. We only send vital information to the LLM, significantly reducing computational costs while increasing service accuracy. We’re continuously refining our model to work reliably in actual medical environments where noise interruptions are common and recording quality varies.
In a real hospital scenario, when a patient says, “My body’s giving me the shivers,” our model can identify the clinically relevant “chill” from the word “shivers.” Even if mispronounced as “shivvers,” the model still recognizes that this conversation contains information pertinent to chills. As doctor-patient conversations happen in real time, all speech is processed by the lightweight model first. When terms like “shivvers” emerge, the model determines if this represents essential clinical information—if important, it’s sent to the LLM for deeper analysis; if not, it’s discarded. We only send vital information to the LLM, significantly reducing computational costs while increasing service accuracy. We’re continuously refining our model to work reliably in actual medical environments where noise interruptions are common and recording quality varies.
CLOVA Healthcare Agent: Reimagining patient care with AI-powered smart wards
In today’s healthcare environment, AI should function not merely as a supplementary tool but as an efficient partner for medical staff providing patient care. Hospital wards face constant patient requests that nurses must address promptly, often while juggling numerous other responsibilities. The CLOVA Healthcare Agent transforms the concept of a smart ward by creating an environment where patients receive timely assistance while reducing the burden on nursing staff.
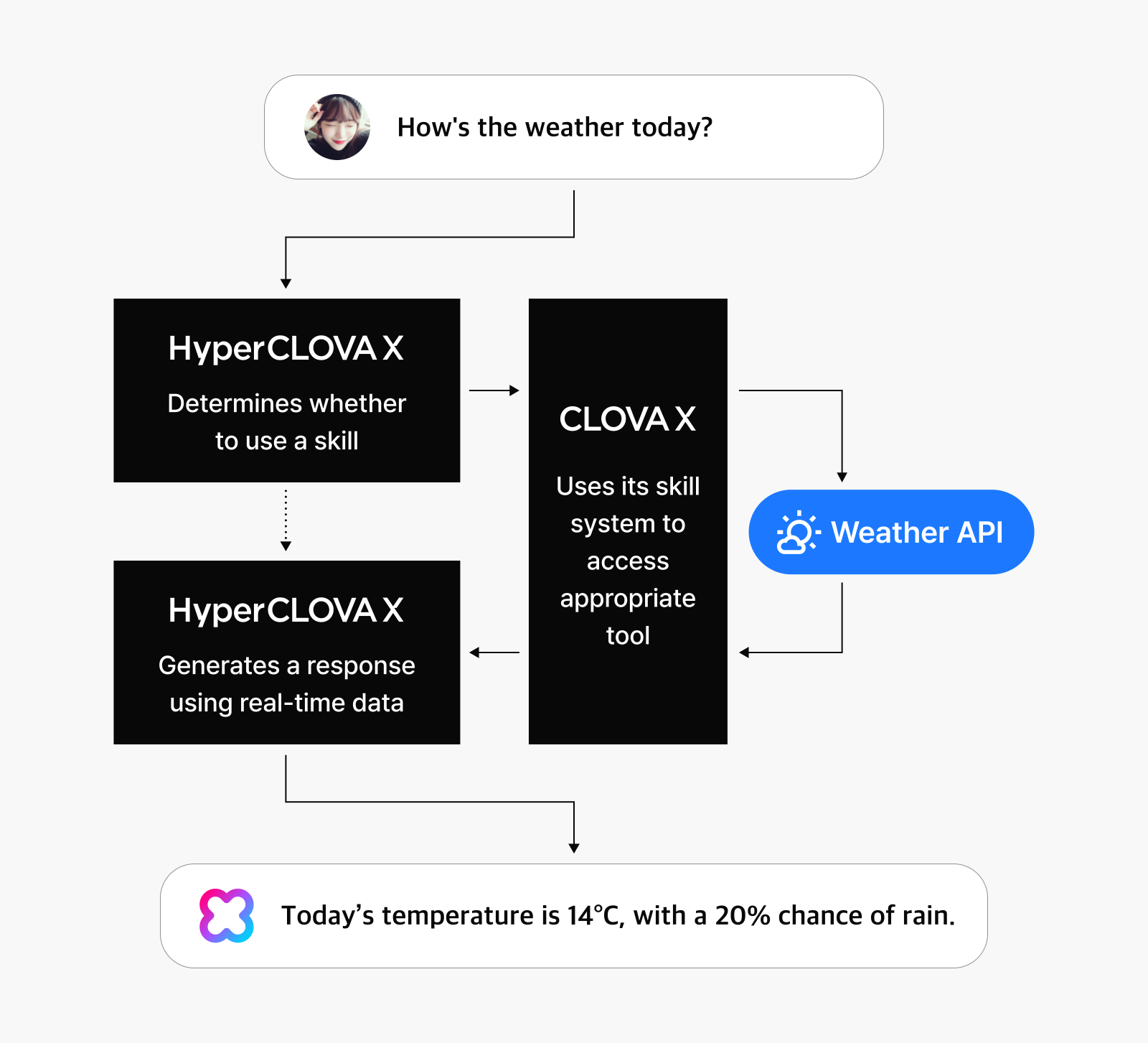
While traditional LLMs simply produce answers to user questions, agents uses enhanced LLM capabilities to generate optimal responses by analyzing requests and independently calling the appropriate models or tools as needed. This fundamental distinction enables meaningful change in medical settings.
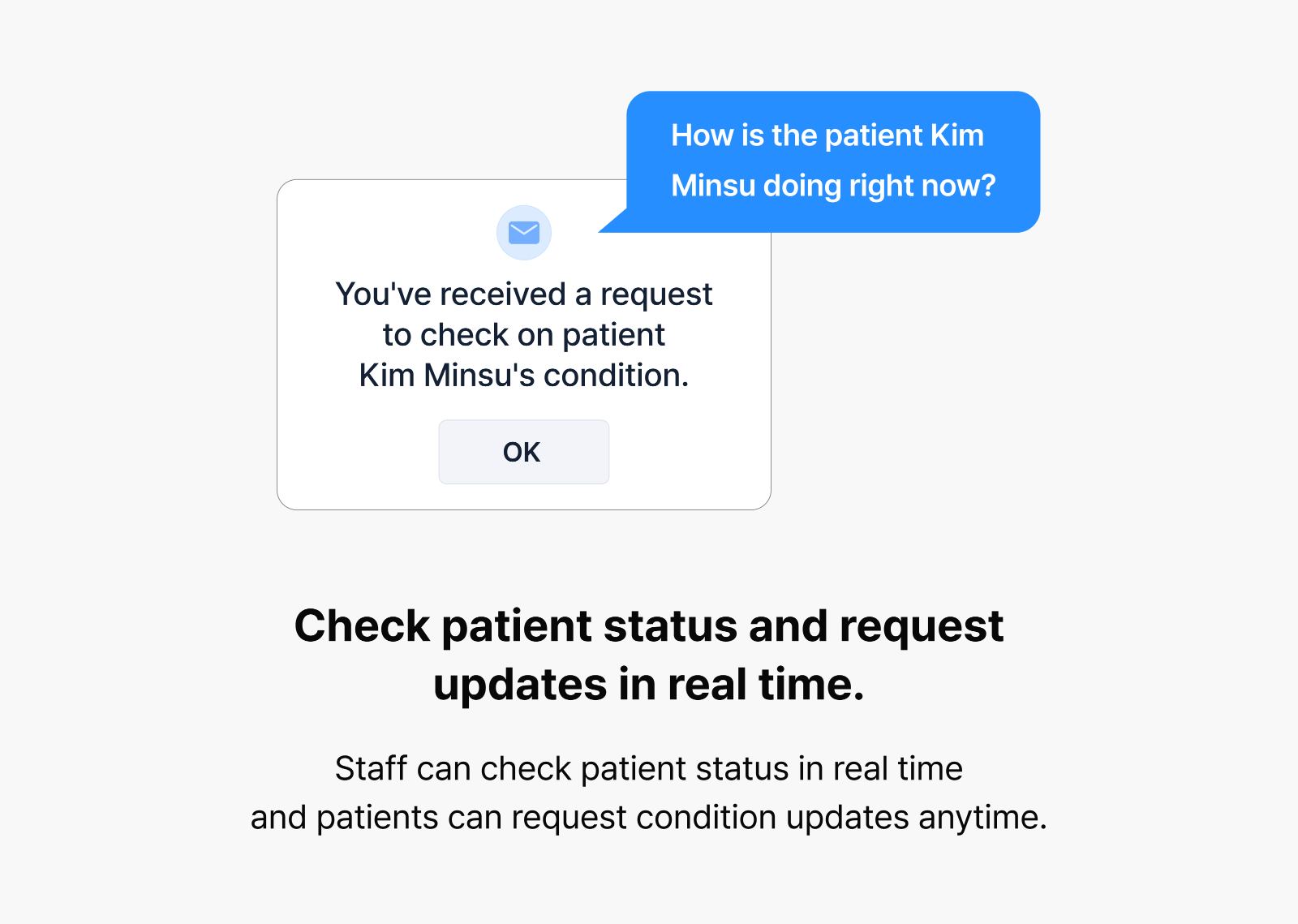
Hyejeong: An agent is a system that automates complex tasks by combining different language models and tools. For example, when a user asks CLOVA X, “How’s the weather today?” the agent recognizes the need for real-time information and independently accesses relevant data through its skill system. In essence, an agent is a dynamic system that can select and leverage appropriate tools based on the context.
The CLOVA Nursing Agent is a ward management service powered by an AI agent to reduce nurses’ workload and help patients receive assistance more efficiently. Unlike traditional hospital AI solutions, it specifically targets daily ward operations to alleviate nursing burden and improve response times for patient care needs.
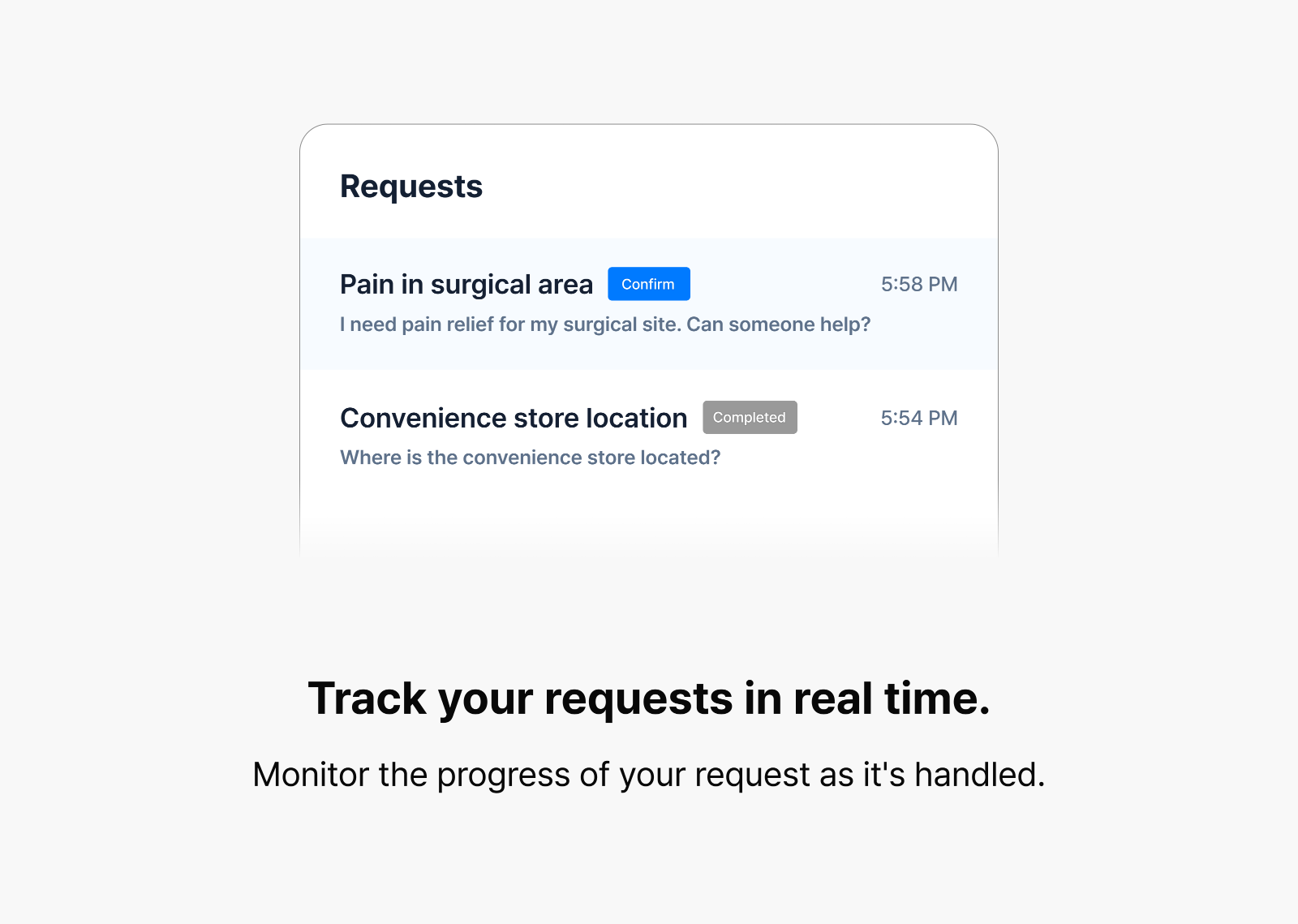
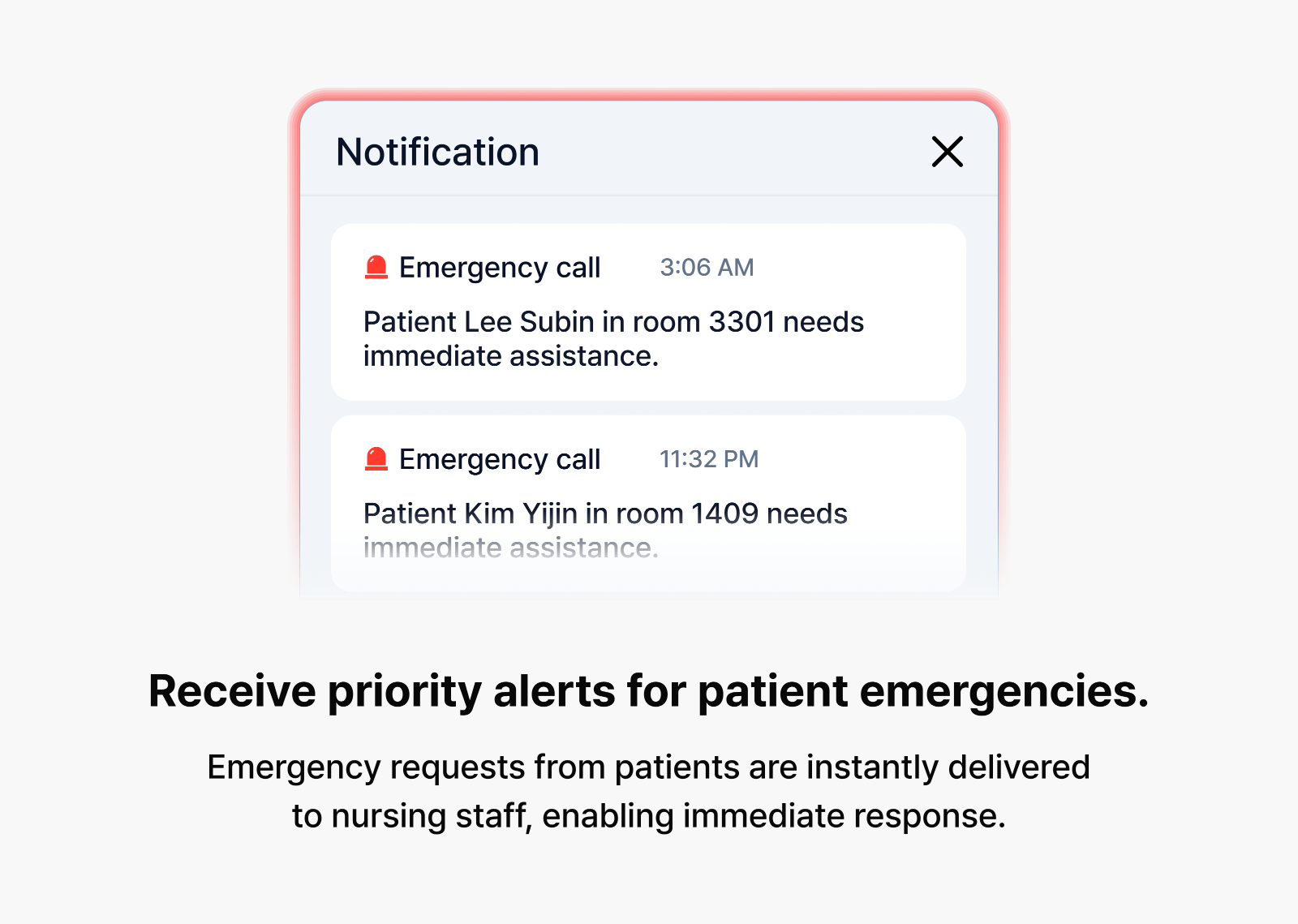
On average, nurses care for 22 patients daily—managing everything from answering repetitive basic questions and monitoring patient conditions to responding to emergencies. With such overwhelming responsibilities, it’s unsurprising that 62% of patients report difficulty getting nursing assistance when needed. In these demanding hospital environments, the CLOVA Nursing Agent provides critical support. When patients make requests via voice or text, the agent analyzes them in real time, prioritizing needs and facilitating faster responses.
Emergency detection with CLOVA Nursing Agent
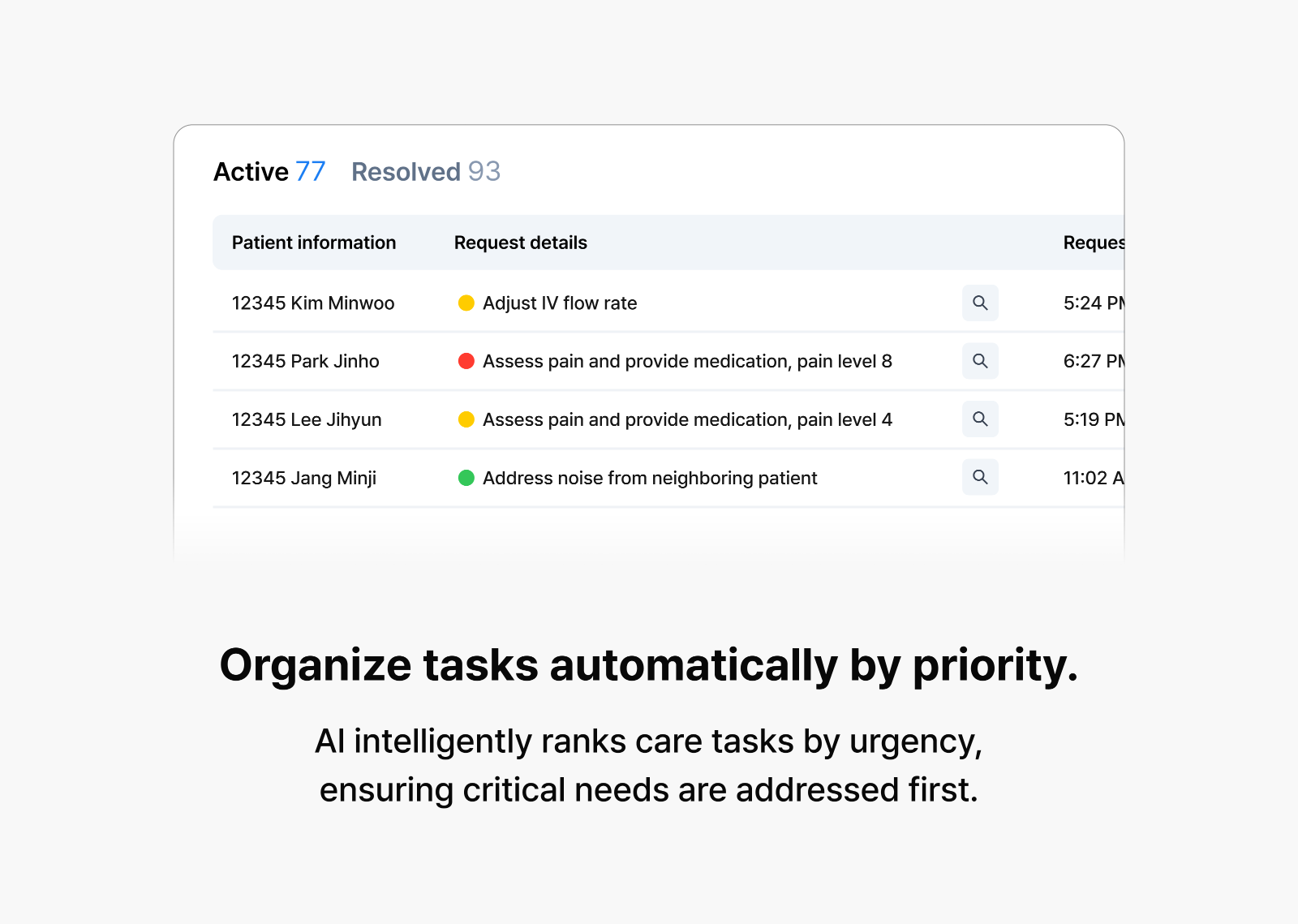
Our planning team’s comprehensive pre-research enabled us to develop a three-tier priority system for patient requests. We categorize Level 0 as low-priority matters such as general inquiries; Level 1 as requests requiring minor treatments or nursing assistance; and Level 2 as emergency situations demanding immediate clinical response. The CLOVA Nursing Agent then communicates these priorities to nursing staff while directly managing tasks within its capabilities. For instance, when patients inquire about discharge procedures, the agent autonomously retrieves and provides relevant information from hospital documentation. When requests lack clarity, the agent asks follow-up questions to ensure proper understanding.
The system employs in-context learning to determine priorities without extensive pre-training. The LLM identifies patterns from contexts to process new requests effectively. For example, when given examples like “Change my pillow” (Level 0), “Replace the IV” (Level 1), and “I can’t breathe” (Level 2), the model learns these classifications. Later, when receiving a request such as “Can you adjust the bed so I can feel more comfortable?” it recognizes similarities to previous examples and assigns priority Level 0. Even in hospital environments with numerous unpredictable variables, the system demonstrates remarkable flexibility in addressing novel situations.
The CLOVA Nursing Agent maintains impressive accuracy rates of 80-90% while continuously improving through regular updates, ultimately enhancing patient care quality.
To learn more, read our previous post on LLM Router: Building a context-aware AI classification system.
Prompt engineering for medical accuracy
For AI to provide reliable healthcare assistance, accurate recognition of patient communication is essential. The CLOVA Nursing Agent is specifically designed to recognize patients’ voices even in noisy multi-person wards, converting patient speech to text using NAVER’s NEST voice recognition engine.
In hospital settings, where each response directly affects patient outcomes, accurate voice recognition is paramount. The CLOVA Nursing Agent employs sophisticated prompt engineering to prevent misinformation by analyzing user intent and context. We continuously refine our prompts to enhance accuracy—essentially instructing the AI what to do and how to do it with maximum clarity.
Our medical checkup chatbot, for example, is set up with prompts that explain rules and limitations with elementary-level clarity when generating responses. While the examples provided here are simplified for demonstration purposes, our actual implementations incorporate a significantly wider variety of scenarios, enabling the AI to handle a comprehensive range of medical situations.
Patient care in 2035: The future envisioned by healthcare researchers
Jaedeok: By integrating wearable devices like smart glasses with CLOVA Voice EMR, doctors will access patient information naturally during appointments. When a doctor asks, “Does it hurt here?” while examining a patient, the AI will precisely locate the point of contact. A multimodal model combining visual and audio capabilities will significantly improve patient-doctor communication.
Hyejeong: The CLOVA Nursing Agent aims to maximize healthcare staff productivity while enhancing patient satisfaction. Once commercialized, nurses can process many requests directly from their station without physically attending to every patient. The system will predict emergency situations in advance and detect subtle changes in patient conditions to alert medical staff promptly. Within a decade, these technologies will help address chronic staffing shortages in healthcare.
Creating a better healthcare future through AI
Hyejeong: My goal with the Healthcare AI team is to apply AI technologies to solve real problems in healthcare settings. Ultimately, I hope this work provides better medical experiences for everyone—hospital staff, patients, and the broader community.
Jaedeok: AI is continuously evolving, presenting new challenges that haven’t been thoroughly researched. The key is approaching new technologies with an open mind. If you’re interested in finding solutions to emerging challenges, watch for our job postings and consider joining us.
The Healthcare AI team remains dedicated to transforming medical environments through AI technology. They’re validating research in real-world settings and developing new technologies, with researchers building invaluable experience along the way. The CLOVA Voice EMR service and CLOVA Nursing Agent have already begun to drive meaningful workplace change, improving healthcare staff productivity and enhancing patient care. We invite you to follow their journey as they create a new medical environment where agent-related technologies, including powerful text and multimodal capabilities, CLOVA’s skills, and browser automation, enable seamless voice communications and AI management to improve healthcare for all.