If you handed your to-do list to AI today, how much could it actually get done? AI can help organize meeting schedules, conduct research, and draft reports—but you’d still need to answer its constant question: “What’s next?”
Recently, though, AI has started evolving beyond simply being a tool that follows orders. It can now determine the next course of action and carry it out on its own. We’re moving from generative AI that waits for your input to agentic AI—systems that autonomously figure out what needs to be done, how to do it, and then act.
What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI with autonomy—it can understand goals and work toward them without humans guiding each step.
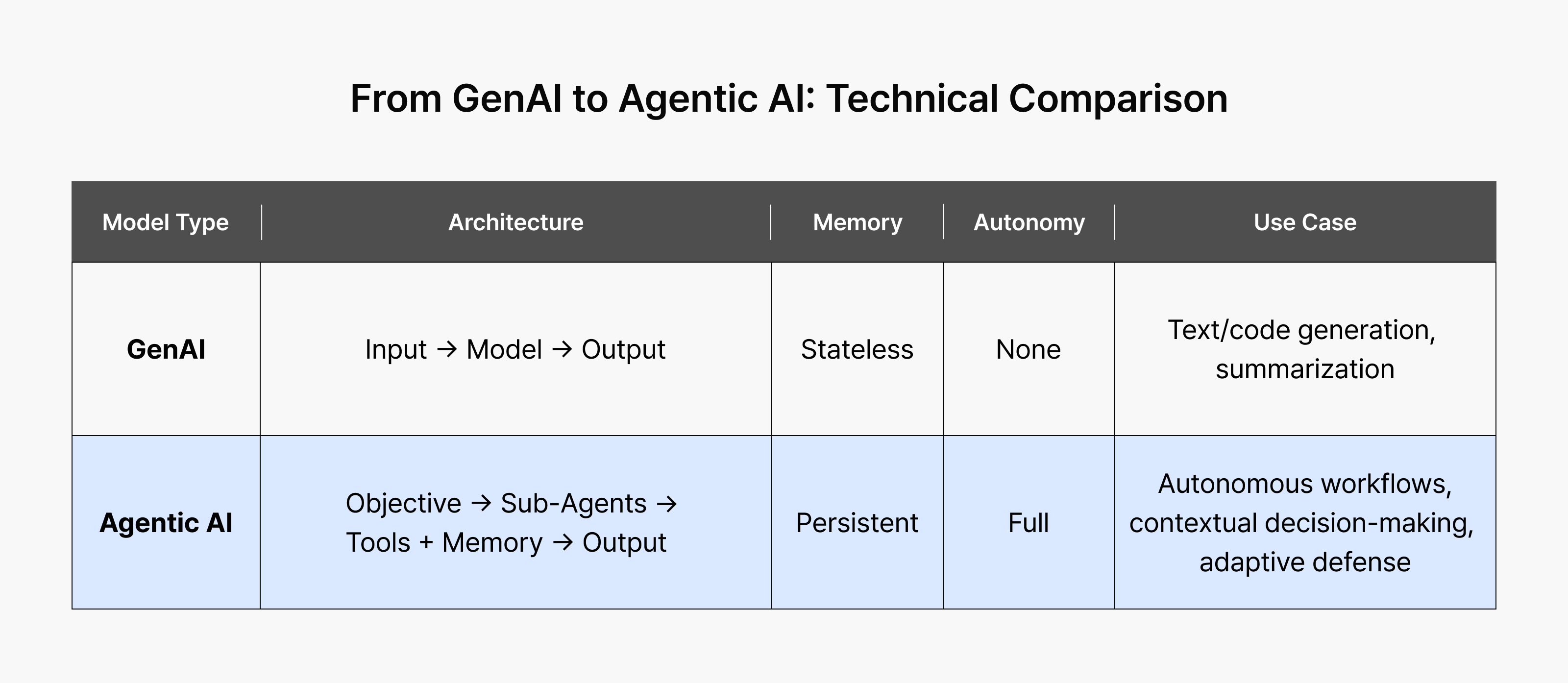
Conventional generative AI can handle a wider range of tasks than earlier systems, but obtaining satisfactory results requires specific instructions from the user. Agentic AI, on the other hand, can autonomously design a process and produce results even when the goal is vague and broad.
For example, when prompted to “organize this week’s meeting agenda,” generative AI would summarize meeting minutes and list key agenda items. It responds to the request and considers the job done. In this way, generative AI acts more like a tool that helps with a specific task.
In contrast, agentic AI asked to “help me prepare for this week’s meeting” doesn’t stop at generating content. It understands the meeting’s purpose and context, then makes decisions and performs tasks in sequence: organizing agenda items, researching relevant data, drafting materials, and setting up the schedule. If necessary, it suggests what to prepare next or even handles it within a predefined scope. Agentic AI acts less like a tool and more like a colleague who helps you move work forward.
An AI service with this kind of autonomy is called an AI agent, and the umbrella term for these autonomous systems is agentic AI.
Figure 1: Comparing generative AI and agentic AI
(Source: Understanding Agentic AI and Its Cybersecurity Applications)
How does agentic AI make decisions and act on its own?
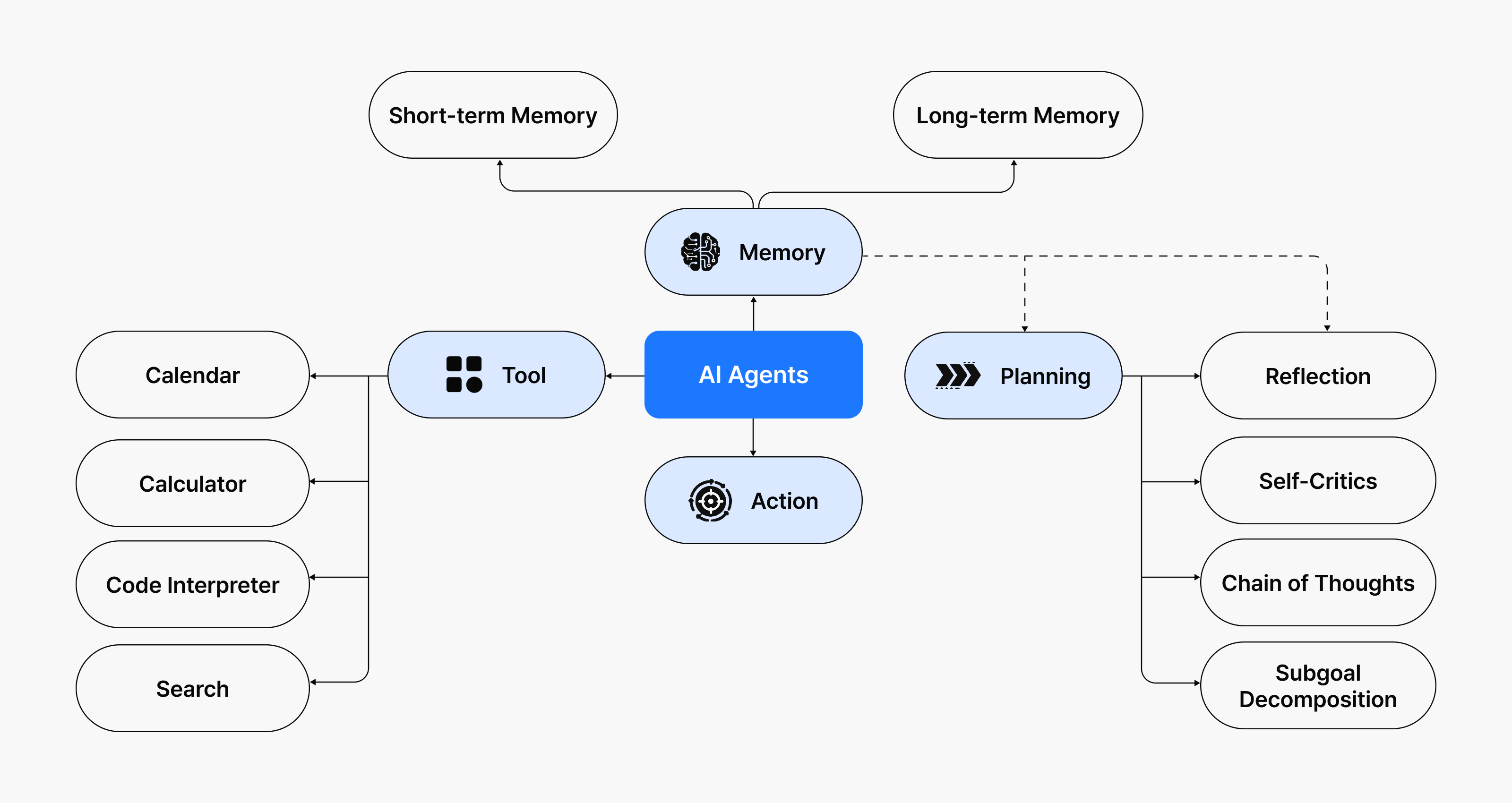
The core capabilities powering agentic AI are reasoning and tool use.
Reasoning
Reasoning models work through three steps: planning, acting, and observing. They make plans, call tools to execute them, then review the results and correct course as needed. This allows them to work through problems step by step and reach answers independently. Rather than simply producing a result, the model creates an internal thought process for how to solve the problem.
Conventional AI attempts to generate answers using fixed resources and the same approach, regardless of the task’s difficulty or complexity. Recent reasoning models, however, can distinguish between a simple task that takes seconds and a complex task requiring sustained autonomy—one that involves making and revising decisions over weeks or months. Based on this assessment, they perform reasoning stages accordingly: plan, act, and self-diagnose.
Tool use
Agentic AI also selects and leverages external tools as needed. This might mean searching the web to retrieve information, querying internal company documents for specific product details, or performing complex calculations using a calculator tool.
By combining reasoning and tool use, the range of tasks AI can handle has expanded dramatically—the reason is why agentic AI is becoming so important.
Figure 2: Explanation of reasoning and tool-using abilities
(Source: Agentic AI Architecture: A Deep Dive For Enterprises)
Why the focus on agentic AI?
Agentic AI is emerging as a key driver of next-generation AI innovation because it can solve problems and review its own work independently, without human intervention.
Until now, AI struggled to solve complex problems on its own. It required developers who understood AI’s capabilities to design services that filled the gaps—supplementing what AI couldn’t handle with additional logic and systems. To users, AI appeared to autonomously solve complex tasks, but in reality, designing the problem-solving process was time-consuming and costly.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, breaks down complex problems into manageable units. If its existing internal knowledge is insufficient, it calls on external tools to obtain the necessary information and continues problem-solving based on the results. Rather than immediately outputting an initial answer, it verifies the validity of its results and corrects them as needed.
By independently defining and executing the problem-solving process without human intervention, agentic AI takes AI’s applicability and scalability to a new level. The areas that AI can cover autonomously expand significantly. This enables AI to operate effectively even in highly complex environments where human intervention is difficult—such as disaster response sites or space exploration—by defining problems and performing tasks once reserved for humans.
We’re already seeing this change in our daily lives and across industries. A coding AI agent, for example, can take a simple request like “build me an app with these features” and autonomously break down the requirements, write code, and fix errors. In customer service, AI agents don’t just answer questions—they understand the customer’s situation, retrieve relevant information, take the next steps to resolve the issue, and transfer to a human when necessary.
In healthcare, AI agents support doctors and nurses in caring for more patients, more accurately, and in less time—organizing patient conditions and identifying needed prescriptions. Agentic AI is evolving into a new kind of colleague that works alongside humans to solve problems across daily life, healthcare, and countless other industries.
TEAM NAVER’s agentic AI
TEAM NAVER is applying agentic AI across nearly every user-facing service, connecting it to real experiences. From NAVER Search and Shopping to Webtoon and Maps, you can encounter agentic AI naturally in any NAVER app.
Say you ask a shopping agent to “do my grocery shopping within this week’s food budget.” It will create a list of ingredients you need, compare prices and benefits, and present the available options. It can go even further—making a payment and suggesting menus based on the items purchased, creating a personalized shopping experience.
Throughout this process, the user doesn’t need to provide step-by-step instructions. They simply share their goal, and the AI figures out the steps and acts autonomously, seamlessly moving from searching to comparing to selecting. Unlike keyword searches or product recommendations, this is agentic AI in action—understanding user intent, making decisions, and acting accordingly.
Challenges of agentic AI: Transforming autonomy into trust
Along with its potential, agentic AI creates new challenges around transparency and safety.
As agentic AI becomes more embedded in our lives, users naturally ask: “Why did it make this choice?” “How did it come up with this plan?” Only when users understand the basis of AI’s reasoning can we ensure transparency—which leads directly to trust.
Safety is equally important. Agentic AI goes beyond suggesting information; it performs actions with real-world consequences like purchasing, booking, posting, and deleting. This means autonomous agentic AI must be designed to require human confirmation before executing such actions.
TEAM NAVER is building a collaborative structure that ensures transparency while delegating tasks where AI excels, and reserving areas where human responsibility is essential. Our goal is to create a trustworthy user experience by achieving the right balance between autonomy and control.
Conclusion
The advent of agentic AI isn’t simply about expanding functionality—it’s about reshaping our relationship with AI. In the past, interaction was one-way: humans asked, then waited for results. With agentic AI, AI can work alongside us, independently assessing situations and offering suggestions.
We’ll keep exploring the question, “How can we work better with AI?” as we enter a new era of collaboration—one where humans and AI leverage their respective strengths together.
Learn more in KBS N Series, AI Topia, episode 5
You can see all of this in action in the fifth episode of KBS N Series’ AI Topia, “Agentic AI: The era of AI that takes initiative.” Jung Kweonwoo, AI Application Tech Lead at NAVER, breaks down these ideas with clear examples and helpful context. It’s a great way to get a fuller picture of what we’ve covered here!