AI technology has advanced remarkably in the last few years, benefiting people in untold ways. While we can’t wait to see what fruits this new technology will bear, using the technology safely and ethically remains an important issue. With our unrelenting commitment to delivering new user experiences, NAVER’s AI technology has opened new doors across different domains. But as with all things, we recognize its imperfect nature and are committed to building safer AI technologically and policy-wise.
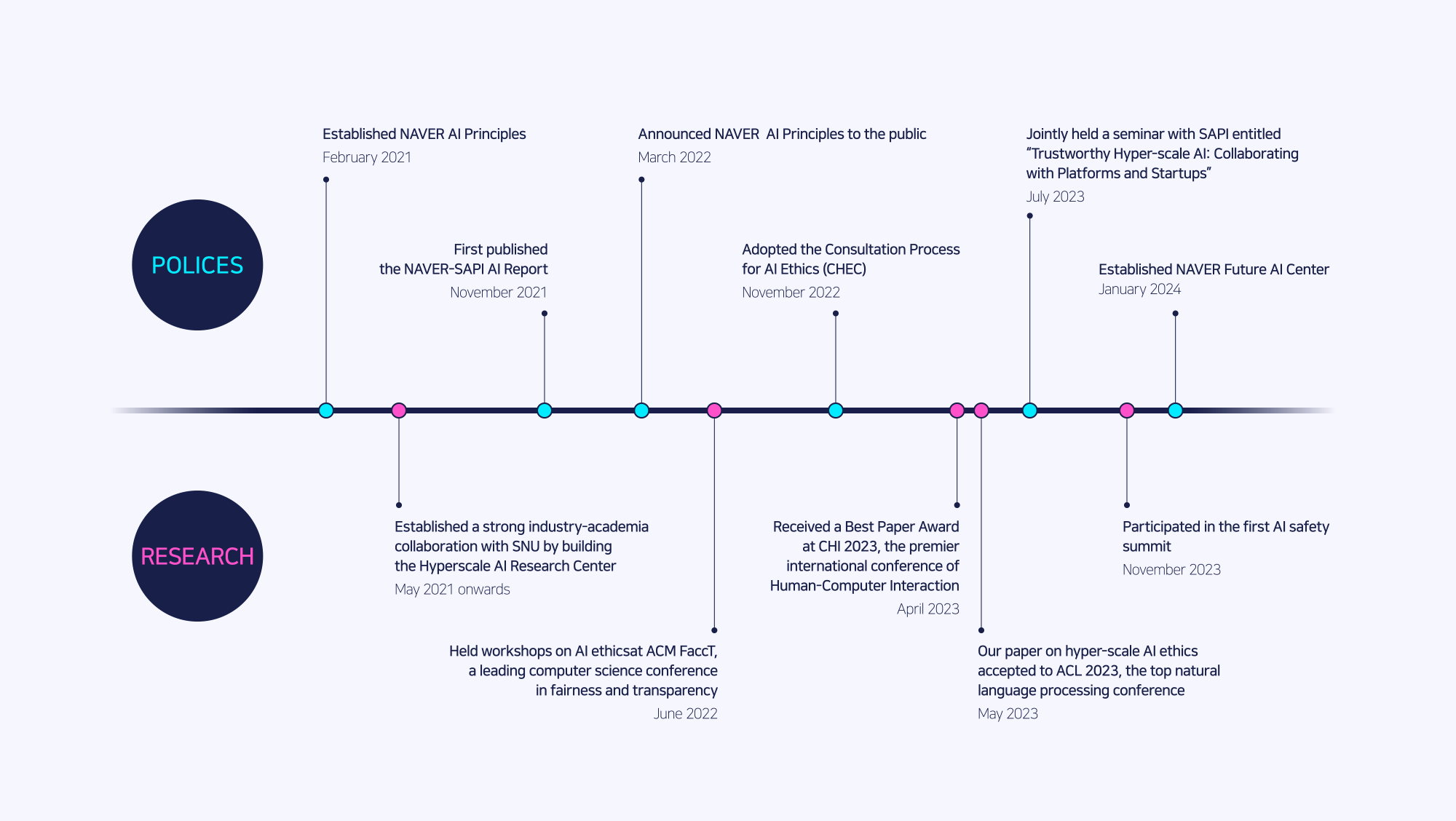
We introduced the NAVER AI Principles when responsible AI was still a relatively new concept. This means we are genuinely committed to a human-centric approach and place people at the center of our AI development. We have also established a consultation process to give everyone here at NAVER a platform for substantive discussions of AI ethics.
Our balanced approach to AI safety merits attention amid global efforts to maximize AI’s potential while minimizing potential risks.
Identifying AI safety risks and promoting ethical AI
What images come to mind when you hear the term AI safety? Perhaps it’s the story in “Matrix,” or the AI assistant Jarvis in “Iron Man.” Or maybe your mind wanders back to a cautionary tale of how AI could outsmart humans. Recently, there has been much talk of frontier AI models, which are general-purpose, large-language models.
In November 2023, the AI Safety Summit was held for the first time to discuss the subject, bringing together representatives from 28 governments around the world, tech executives of leading AI companies, academics, researchers, and heads of nonprofits. Let’s take a deeper dive into what they identified as the risks to AI safety and how we can enforce the ethical use of AI.
*Three types of risks to AI safety
1. Technological limitations
The first and most immediate challenges come from AI models producing hallucinations, learning from sensitive or biased data, propagating hate speech, and training on copyrighted material without permission. To overcome such limitations, we must ensure that AI models are aligned with human values by ensuring that the training data is accurate and meets strict standards through continuous research.
2. Misuse risks
Second, misuse risks arise when people use AI capabilities with malicious intent as a tool to spread disinformation or scam other people. We can mitigate this type of risk by regulating AI to prevent bad actors from misusing AI and drafting policies and guidelines while educating users on the safe use of AI.
3. Loss of control risks
Third, frontier AI capabilities are available via open source, making monitoring AI for indiscriminate use difficult. As AI gets hyper-intelligent, people may vest too much power in the hands of AI or leave decision-making to AI altogether, which could lead to loss of human control.
As a frontier AI model—and just the third hyper-scale generative AI model in the world—HyperCLOVA X has contributed to the AI field by conducting over 300 research studies over the past five years and achieving meaningful results in top-tier conferences worldwide. In 2023, NAVER participated in the AI Safety Summit to show our commitment to AI safety. Join us in our journey for AI safety in the rest of the blog.
* Our efforts towards safer AI
In January this year, NAVER opened the Future AI Center. NAVER’s Future AI Center is dedicated to AI safety research, and we collaborate with researchers from across the globe to pursue responsible AI and shape trustworthy policies around the technology. We’re working to enhance the capabilities of our AI models with quality datasets grounded on AI safety and rigorous testing.
1. Red teaming AI systems
Red teaming is a form of adversarial AI testing. Our red team prepares our AI models against attacks not just through safety filters and data refinement but also by probing them for failures. We do this by thinking like malicious attackers—deliberately provoking HyperCLOVA X to see whether it makes biased or discriminatory remarks, generates inaccurate information, or gives irrelevant answers. We work to create safer AI models by regularly testing in 14 areas, including hate speech, violence, biased information, factual inaccuracies, and copyright infringement.
※ AI safety standards
 * A red team deliberately plays the role of an attacker to test technologies and services for vulnerabilities.
* A red team deliberately plays the role of an attacker to test technologies and services for vulnerabilities.
2. Preventing AI from disrupting elections
Something that comes up again and again when talking about AI safety is fake news. As voters in more than 50 countries are expected to head to the polls this year, calls for regulation are growing. NAVER strives to ensure that AI-generated content is not used to spread disinformation or defame candidates. We work to ensure that all election-related, AI-generated content carries a disclaimer, and we are also looking to join the C2PA so that digital content can be traced to its origin. At the same time, we are developing technologies of our own to invisibly watermark and label content made with generative AI.
3. Fostering an ethical AI ecosystem
We are interested in AI ethics and have long conducted research to tackle AI safety. We share the source code and datasets to make what we learned in our research available to the public. At the same time, we ensure that individuals do not duly rely on AI so as to lose their decision-making abilities by providing training courses on the safe use of AI. We also introduced CLOVA CareCall, our AI-enabled telephone reassurance service that checks in on people who need care, which has already proven that AI can make a difference in social and public health.
Aligning with the broader international community
At NAVER, we are concerned over foundational ethics in the IT industry and beyond. Researchers discuss AI safety with great zeal, but agreeing on how to shape and apply the standards can be challenging. This is why we need to test different ideas and heed different voices to build an international consensus on how to govern AI technology. Our endeavor to create a safe HyperCLOVA X continues beyond Korea as we join an industrywide effort worldwide with the UN, the EU, the UK, the US, Canada, the Middle East, and the rest of the world toward safer AI.